Plant-A-Plant Introduction
Plant Growth from a Seed
A plant seed contains its own life support system. When stimulated to germinate, seeds use stored food reserves and surrounding oxygen to grow into sprouts. A sprout is a tender, often edible seedling that is produced following seed germination. As the sprout begins to develop and use up its stored reserves, the seedling becomes totally dependent on environmental sour
 ces
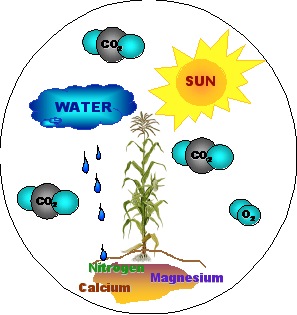
of energy and material. Plants need light,
carbon dioxide, water and additional mineral nutrients to continue
growth after germination.
ces
of energy and material. Plants need light,
carbon dioxide, water and additional mineral nutrients to continue
growth after germination. What keeps plants growing?
The major requirements for plants to grow are light, water, and carbon dioxide. These components are used in the process of photosynthesis. Photosynthesis (derived from Greek fós, fótos – ‘light’ and synthesis – ‘fusion’, ‘composition’) is a process, where absorbed sunlight is converted to chemical energy, which is then used to incorporate carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are simple and compound sugars, such as cellulose that make up the main plant structure. This process of taking CO2 out of the atmosphere and converting it to carbohydrates actually locks up the carbon in plant tissues, storing it until that plant dies. If you were to dry a plant, 45-50% of the plant mass, also called biomass, is made up of carbon.

In addition to light, water and carbon dioxide, plants also require small amounts of other nutrients and minerals for plant structure and function. For example, proteins require nitrogen and sulfur while chlorophyll, necessary for photosynthesis, requires magnesium. Of these nutrients, nitrogen is the most important, representing up to 5% of plant dry mass.
What affects the rate of photosynthesis?
Photosynthetic rate is the parameter, which describes the amount of carbon dioxide consumed by a leaf, measured in units of g (CO2) per m2. The rate of photosynthesis can be affected by any of the factors discussed above including sunlight, temperature, water, availability of CO2 and O2 or the macro and micro nutrients that influence the production of chlorophyll and other chemical compounds taking part in photosynthesis. At any one time photosynthetic rate is being limited by the availability at least one factor. A factor is regarded as a limiting to growth when even though all other factors are in normal concentrations the process of photosynthesis is slowed down, altered, or stopped.
Hands-on Photosynthesis Experiments
During the Plant-A-Plant Classroom Experiments students will watch seeds grow into sprouts and then manipulate environmental conditions to see how different factors affect plant growth. Students’ work during these experiments should help them understand how each important factor for photosynthesis affects plants when it is in short supply.
Experiments are designed so they can be done by individuals, small groups, or as a class. Individual experiments can be performed independently, in succession or in conjunction. If more than one experiment is completed it will be interesting for students to draw conclusions between experiments. Asking questions like, which factor seems be the greatest limitation to growth? While these experiments do not provide a lot of opportunity for inquiry, following the precise procedures will give students the tools they need to create their own experiments. A well thought out discussion of experimental results should also lead students to the formation of their own research questions about plant growth and resource availability, which can be tied to other topics including the carbon cycle and climate change.